JDBC
There are 4 types of JDBC drivers:
- JDBC-ODBC bridge driver
- Native-API driver (partially java driver)
- Network Protocol driver (fully java driver)
- Thin driver (fully java driver)
1.DriverManager class:
The DriverManager class acts as an interface between user and drivers. It keeps track of the drivers that are available and handles establishing a connection between a database and the appropriate driver.
The DriverManager class maintains a list of Driver classes that have registered themselves by calling the method DriverManager.registerDriver().
2.PreparedStatement:
The PreparedStatement interface is a subinterface of Statement. It is used to exeucte parameterized query
3.ResultSetMetaData:
The metadata means data about data i.e. we can get further information from the data
4.DatabaseMetaData :
DatabaseMetaData interface provides methods to get meta data of a database such as database product name, database product version, driver name, name of total number of tables, name of total number of views etc.
5.ParamterMetaData :
6.Callable Statement
A stored procedure is nothing more than prepared SQL code that you save so you can reuse the code over and over again.
Creating Procedure
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE AllEmp()
BEGIN
SELECT * FROM emp;
END //
DELIMITER ;
Calling Procedure
call AllEmp();
y := x*x Here → x is IN paramerer, y is OUT Parameters
x := x*x* Here → x is INOUT Parameter
1.Using In Parameters(Passing Parameters to Input)
DELIMITER // call GetEmpbyID(2)
CREATE PROCEDURE GetEmpbyID(IN sid INT)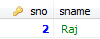
BEGIN
SELECT * FROM emp e WHERE e.sno = sid;
END//
DELIMITER ;
2.Using OUT paramaters(It Returns value as Result)
DELIMITER // call GetEmpCountbyID(2,@x)
CREATE PROCEDURE GetEmpCountbyID(IN sid INT, OUT cnt INT)
BEGIN
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM emp e WHERE e.sno = sid;
END//
DELIMITER ;
In JDBC for Excecuting procedure we have Callablestatement
For OUT parames → cs.registerOutParameter(2, Types.INTEGER);
For IN parames → cs.setInt(1, 2);
7.Batch Processing :
Instead of executing a single query, we can execute a batch (group) of queries. It makes the performance fast.
The java.sql.Statement and java.sql.PreparedStatement interfaces provide methods for batch processing.
Methods:
void addBatch(String query) → It adds query into batch.
int[] executeBatch() → It executes the batch of queries.
if query Success → 1
query Failed → 0 for each query
8.Transaction Management in JDBC
9.ResultSet
we have 2 types of ResultSets
1.Scrollable ResultSet : any Direction retrieve data
2.NON-Scrollable ResultSet(Default) : Single Direction Retrieve Data
rs.absolute(4); → It Points to Exact 4th index in ResultSet
rs.relative(4); → It points to 4th index from the current Location
10.BLOB(BinaryLarge Object)
→ used for Storing multimedia data like Images, Audio, video Files in database
Methods:
1.Inserting :
1) public void setBinaryStream(int paramIndex,InputStream stream) throws SQLException
2) public void setBinaryStream(int paramIndex,InputStream stream,long length) throws SQLException
2.Retriving
Blob b=rs.getBlob(2);
11.CLOB(CharacterLarge Object)
→ used for Storing Files in database
Insert : setCharacterStream(2,Stream);
Retrive :public Clob getClob(int columnIndex)
12.Connction pooling
Connction Pooling works with Application server